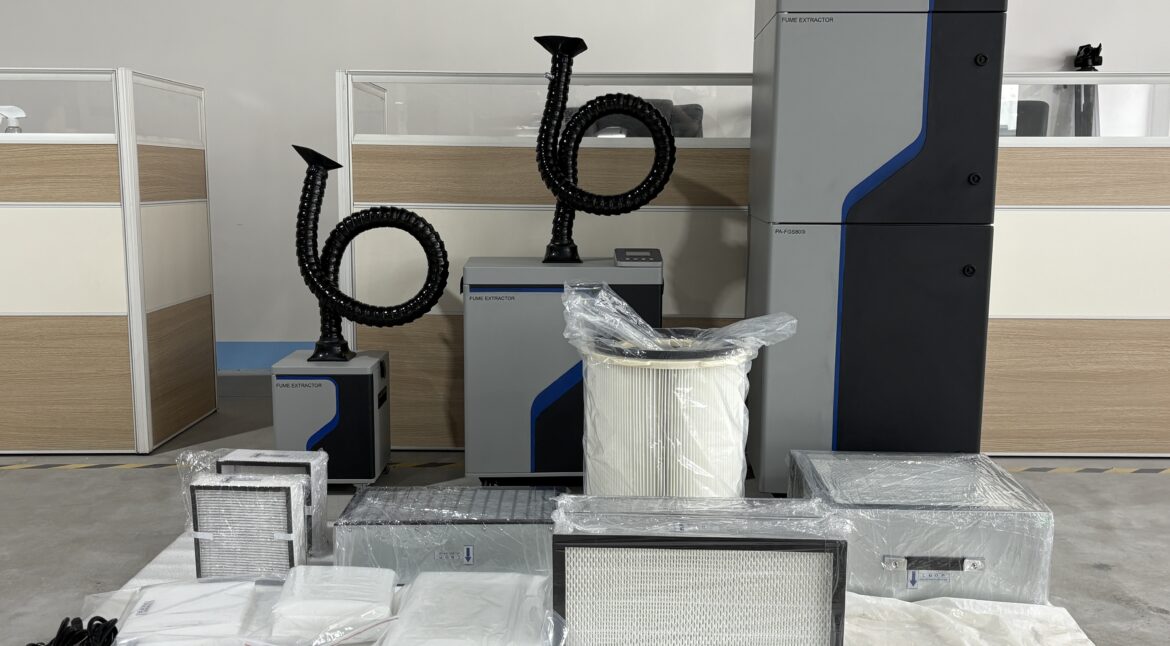
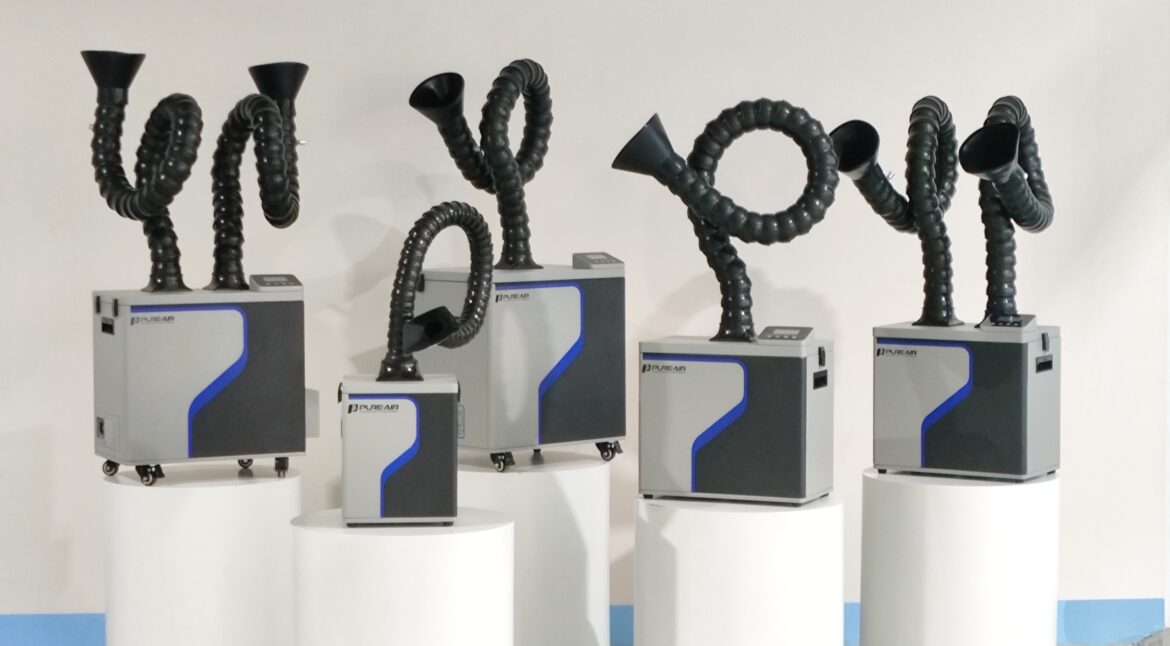
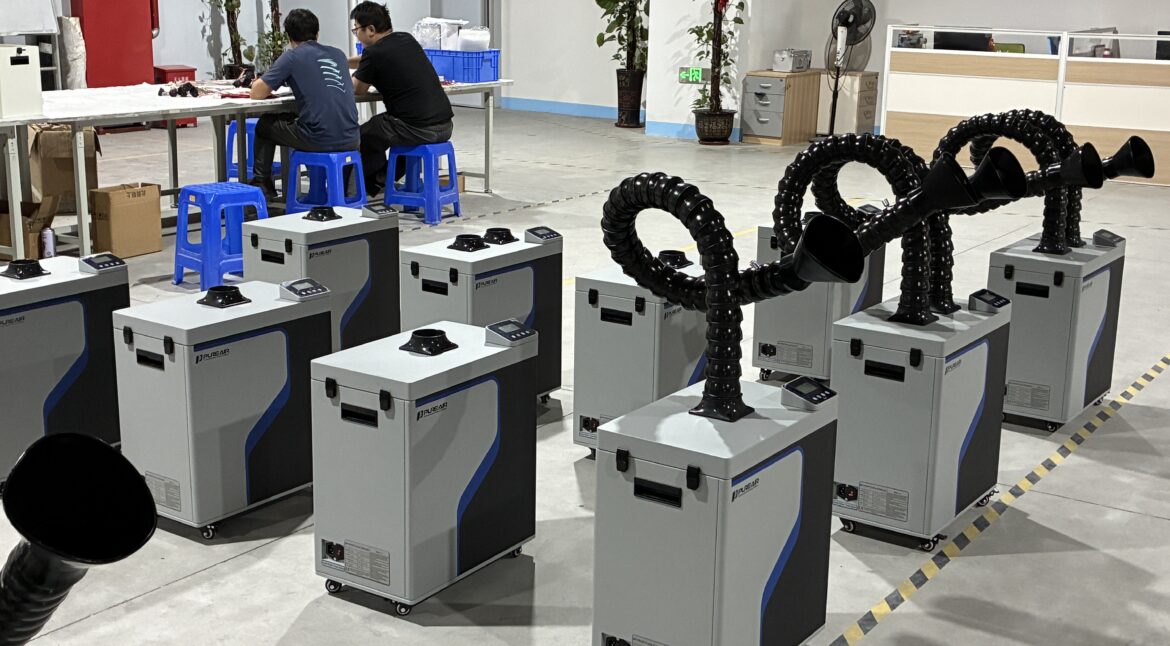
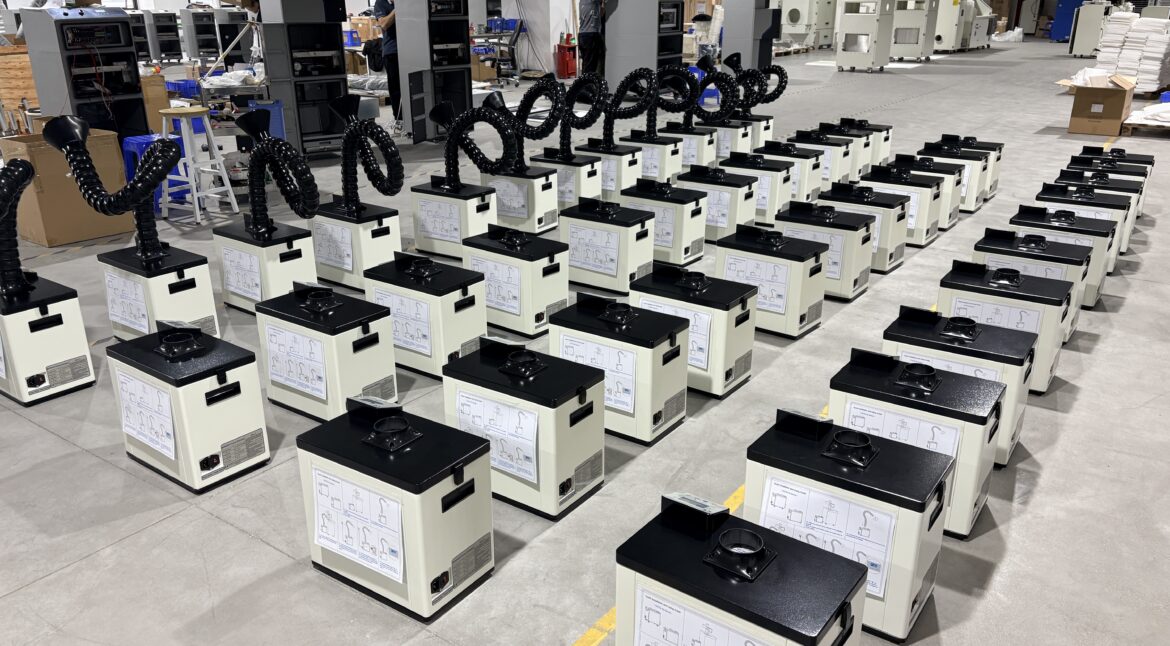
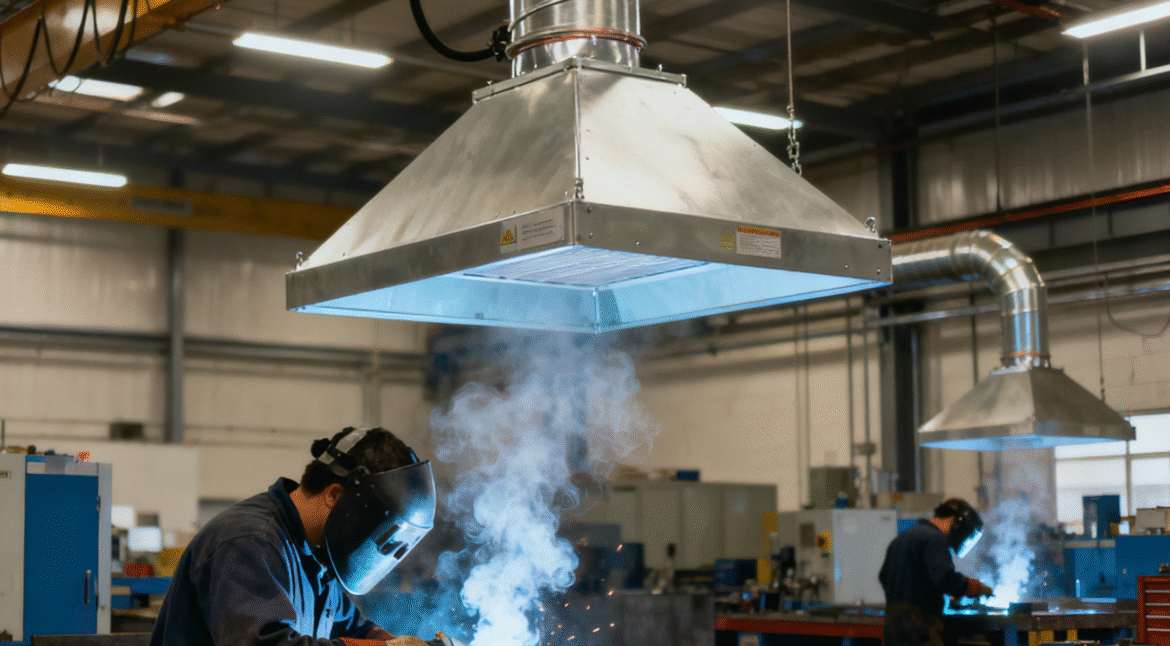
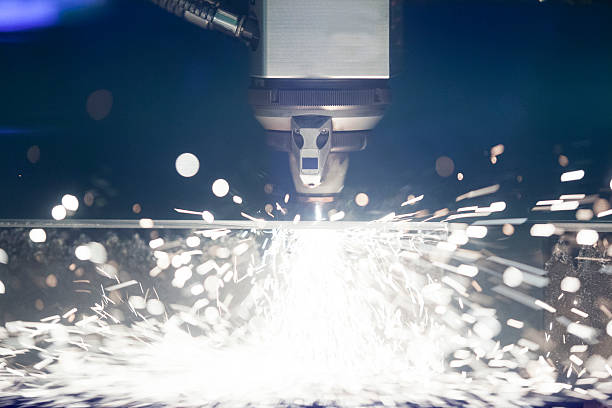
Core Structure of PURE-AIR Industrial Fume Extractor Introduction The performance and reliability of an industrial fume extractor depend not only on filtration efficiency, but also on the overall system structure and component integration. A well-engineered internal structure ensures stable airflow, efficient pollutant capture, long service life, and safe continuous operation.…
How to Control Soldering Smoke in Electronics Manufacturing Introduction Soldering is a core process in electronics manufacturing, used extensively in PCB assembly, component repair, and production lines. However, soldering operations generate smoke, fine particles, and chemical vapors that pose serious risks to operator health, product quality, and workplace compliance. Effective…
Fume Extraction Solutions for Laser Cutting Machines Introduction Laser cutting machines are widely used in metal processing, signage production, electronics manufacturing, and industrial fabrication due to their high precision and efficiency. However, laser cutting also generates a significant amount of smoke, fine particulate matter, and harmful gases, which pose serious…
Advanced Purification Strategies for Stainless Steel Welding Chrome Fume and Laser Cutting Nano-Dust
In the modern precision manufacturing landscape, stainless steel processing stands as a cornerstone of high-end engineering. However, the very alloying elements that make stainless steel resilient—specifically chromium and nickel—create a formidable health hazard when subjected to the extreme heat of welding and laser cutting. During these processes, the air is…
Behind every high-precision industrial process lies a hidden risk. Thermal operations such as laser cutting, welding, and plasma gouging drive efficiency, yet introduce serious hazards. As production continues, workshops can rapidly fill with sub-micron metal dust, carcinogenic gases, and volatile organic compounds. More critically, when fine metallic particles accumulate, they…
Why High Negative Pressure Matters in Fume Extraction Introduction In industrial environments, effective fume extraction is not determined by airflow volume alone. One of the most critical—and often misunderstood—factors is high negative pressure. Many standard ventilation systems fail to capture hazardous fumes efficiently because they cannot maintain stable suction under…
Introduction Industrial production processes generate a wide range of airborne pollutants that are often invisible but highly hazardous. Smoke, dust, and harmful fine particles are common by-products of laser processing, welding, soldering, grinding, and other manufacturing operations. Without effective control, these contaminants can seriously impact worker health, equipment reliability, and…
What Is an Industrial Fume Extractor and How Does It Work? Introduction In modern manufacturing environments, airborne pollutants such as smoke, fumes, fine dust, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are unavoidable by-products of industrial processes. Laser cutting, welding, soldering, engraving, and chemical processing all generate hazardous fumes that can pose…
In the vanguard of advanced manufacturing, laser cutting and metal 3D printing (Additive Manufacturing) have revolutionized production speed and geometric complexity. However, these high-energy processes generate a byproduct that is as dangerous as it is invisible: sub-micron metallic fumes and plastic aerosols. These particles, often smaller than $0.1\mu m$ (nanoparticles),…
n the industrial world, safety managers often find comfort in numbers. When purchasing fume and dust extractors, the focus typically gravitates toward the filter specification—specifically the high-efficiency ratings like HEPA (99.97%) or MERV 16. However, relying solely on the filter’s efficiency to protect employees is a dangerous oversight. Even if…