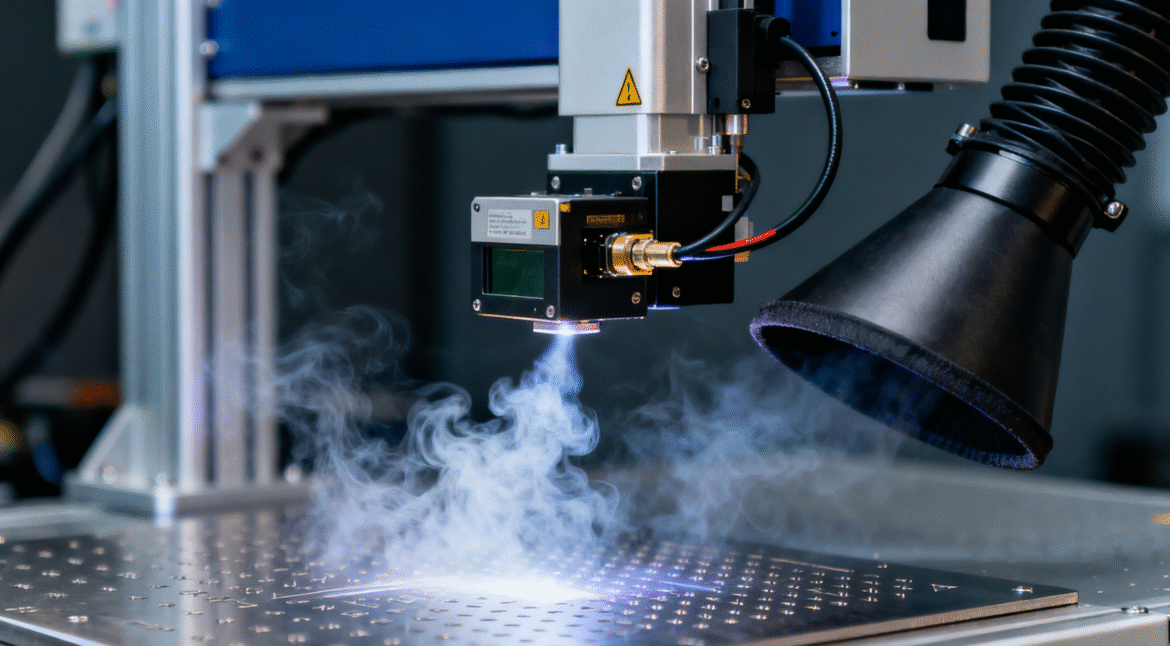
Air quality impacts productivity, safety, and compliance across all manufacturing sectors. Therefore, factories continue to invest heavily in high-efficiency fume purifier solutions that capture harmful particles at the source. As manufacturing complexity grows, many buyers must choose between electrostatic fume purifiers and HEPA filtration systems. Although both technologies remove airborne pollutants, they operate through different mechanisms, deliver different performance values, and support different factory conditions. Consequently, understanding their strengths and limitations helps buyers make informed and cost-effective decisions.
Why Factory Air Filtration Demands Reliable Technology
Factories generate multiple fume types. Welding produces metal oxide particles. Soldering releases sticky rosin fumes. Laser cutting creates ultra-fine particulates. However, printing, chemical processing, lithium battery manufacturing, and textile production release additional pollutants that threaten workers and equipment. Because each pollutant behaves differently, filtration systems must offer stable removal efficiency across long production cycles.
Industrial procurement teams therefore prioritize technologies that maintain airflow, reduce maintenance downtime, control long-term operating costs, and meet strict environmental rules. This context explains why the comparison between electrostatic and HEPA technology remains central to modern industrial air purification planning.
Understanding Electrostatic Fume Purifier Technology
Electrostatic fume purifiers use high-voltage ionization to charge airborne particles. These charged particles then move toward the collection plates with the opposite polarity. As they attach, the plates retain them until technicians clean the modules. Because electrostatic force attracts extremely small particles, this method remains effective for sub-micron pollutants.
Electrostatic purifiers maintain stable resistance levels. Airflow does not drop significantly because the system does not rely on dense media filters. This airflow advantage supports continuous production lines, where ventilation performance must stay consistent for shift-long operations.
Furthermore, electrostatic technology handles sticky fumes efficiently. Soldering, laser marking, and plastic cutting release sticky aerosols that clog traditional filters quickly. Electrostatic plates allow these particles to settle without blocking airflow. Therefore, factories that handle fine oily fumes often prefer electrostatic systems.
Understanding HEPA Filtration for Industrial Use
HEPA filtration uses dense mechanical media to trap particles physically. Each fiber layer intercepts, impacts, or diffuses airborne particulates. Because the filter density is high, HEPA delivers consistent capture rates for particles down to 0.3 microns. Although HEPA originated in cleanroom and medical fields, industrial buyers now use it widely due to its stable and predictable performance.
However, HEPA filtration restricts airflow as particles accumulate. As resistance rises, fans must work harder to maintain airflow. Therefore, maintenance frequency increases, which affects operational costs. Factories that run continuously experience more frequent filter replacements, especially when dealing with oily or sticky fumes.
Nevertheless, HEPA filtration remains a reliable choice for dry dust, powder handling, sensitive electronics, pharmaceutical production, and lab-grade purification tasks. Its mechanical nature ensures stable performance as long as filters are replaced on time.
Performance Comparison in Real Factory Scenarios
Selecting the better technology requires understanding how each system behaves in actual factory conditions. Different applications expose filtration systems to different particle behaviors, temperatures, and chemical compositions.
Welding Workshops
Welding fumes contain metal oxides, ultra-fine particles, and occasionally oily content. Electrostatic fume purifiers capture these particles efficiently because their ionization chambers attract ultra-fine particles easily. Because sticky fumes accumulate on plates instead of dense filters, maintenance stays predictable. Meanwhile, HEPA filters clog faster in heavy welding environments because oil and metal dust restrict airflow.
Soldering Lines and Electronics Production
Soldering fumes contain sticky rosin aerosols. HEPA filters fail quickly because adhesive particles block airflow. Conversely, electrostatic solutions handle rosin aerosol consistently. Therefore, electronics manufacturers often adopt electrostatic fume purifiers for long-cycle production.
Laser Cutting and Laser Marking
Laser processes release ultra-fine particulates that require high-efficiency capture. Electrostatic purifiers capture these particles without losing airflow. However, some laser systems use HEPA systems as final-stage filtration when ultra-high purity is required. A hybrid system sometimes provides the best balance.
Chemical Production and Pharmaceutical Plants
HEPA filtration performs well in controlled environments. It offers predictable performance against dry dust, powder, and non-sticky aerosols. Electrostatic systems are less common in these sectors because chemical fumes may damage ionization modules. Therefore, HEPA technology suits pharmaceutical production better.
Textiles, Plastics, and General Manufacturing
These industries generate mixed particles. Electrostatic systems handle fine aerosols and semi-sticky particles efficiently. HEPA systems work well with dry dust. The ideal choice depends on the dominant pollutant type.
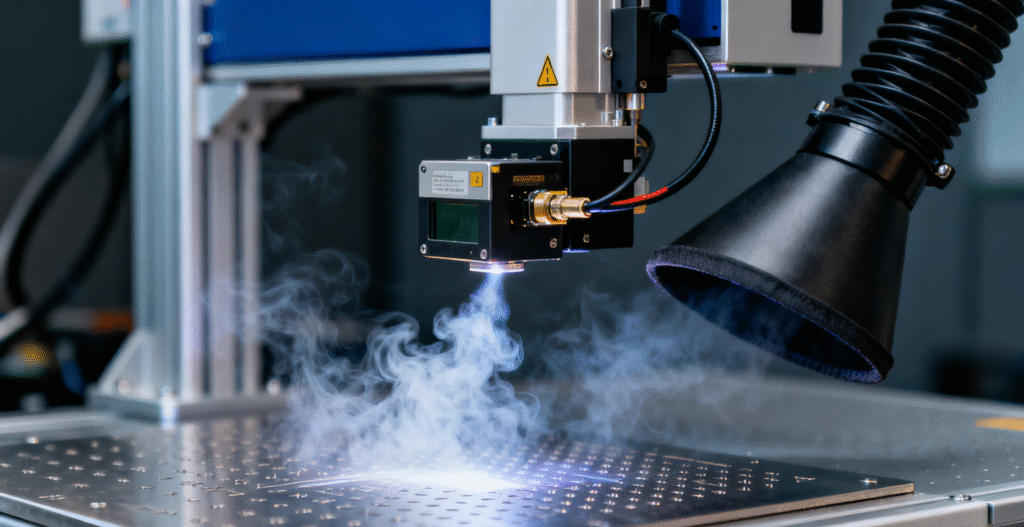
Maintenance and Operating Cost Considerations
Maintenance strongly influences long-term ownership cost. Electrostatic fume purifiers reduce waste because technicians wash and reuse collection plates. Although the ionization module requires periodic cleaning, the interval stays longer than HEPA filter replacement cycles. Because of this, factories with high-volume fume emissions often prefer electrostatic solutions to control operating costs.
Meanwhile, HEPA systems require frequent filter changes. Replacement filters increase cost, especially when clogging accelerates under heavy loads. Although HEPA systems offer predictable performance, buyers must factor consumable costs into long-term budgets.
Additionally, clogged HEPA filters reduce airflow. Reduced airflow increases fire risk, lowers capture efficiency, and places stress on fans. Therefore, maintenance scheduling must remain strict.
Energy Efficiency and System Stability
Energy efficiency affects budgeting, especially in factories operating 24 hours daily. Electrostatic systems maintain constant resistance, which reduces fan workload. Because airflow stays stable, energy consumption remains predictable. HEPA systems consume more energy as resistance rises. Therefore, factories using HEPA filtration must size fans correctly and monitor resistance regularly.
System stability also matters. Electrostatic purifiers can maintain consistent filtration under heavy aerosol loads. HEPA systems maintain predictable efficiency only when filters remain clean. Because filter clogging alters performance curves, HEPA buyers must accept more variable output.
Environmental Impact and Waste Reduction
Sustainability influences industrial procurement today. Electrostatic purifiers reduce waste because the plates are reusable. Cleaning generates minimal environmental burden. Meanwhile, HEPA systems produce large volumes of spent filters. These filters may contain hazardous materials, which require proper disposal. Therefore, electrostatic solutions support long-term environmental goals more effectively.
However, HEPA filtration suits applications requiring strict regulatory compliance. Waste volume increases, but reliability justifies the environmental cost.
System Integration and Installation Requirements
Electrostatic fume purifiers integrate well with centralized and single-station extraction systems. They support flexible duct routing and maintain stable airflow across long distances. Meanwhile, HEPA systems require stable pressure environments. Long ducting increases resistance significantly. Therefore, HEPA filtration supports compact setups better than long-distance extraction.
Factories should evaluate the layout, duct length, workstation number, and required airflow before selecting technology.
Safety Considerations and Regulatory Requirements
Both systems support industrial safety goals. Electrostatic purifiers include high-voltage modules, yet modern designs follow strict insulation and shutdown protections. HEPA systems contain no electrical ionization risks but require careful fire prevention because clogged filters raise the temperature.
Regulatory bodies accept both technologies. However, some industries demand absolute particle control. In these fields, HEPA systems may serve as mandatory secondary filtration.
Which Technology Is More Reliable for Factory Applications?
Reliability depends on pollutant type, operating hours, airflow needs, and budget considerations. Electrostatic fume purifiers deliver excellent performance for metalworking, soldering, plastics, and laser applications. They maintain low resistance, reduce maintenance, and support long production cycles. HEPA filtration delivers predictable performance for dry dust, pharmaceuticals, labs, and sensitive chemical applications. Each system offers strengths under the correct conditions.
Conclusion
Electrostatic and HEPA technologies both support high-efficiency fume purifier solutions for factories. Electrostatic systems offer better long-term stability for sticky fumes, oily aerosols, and high-load production environments. HEPA systems deliver predictable performance for dry-dust and cleanroom-grade applications. Factory buyers must analyze pollutant type, maintenance targets, environmental rules, and long-term operating costs before selecting a solution. By matching technology to production needs, factories achieve cleaner air, safer environments, and more reliable production performance.