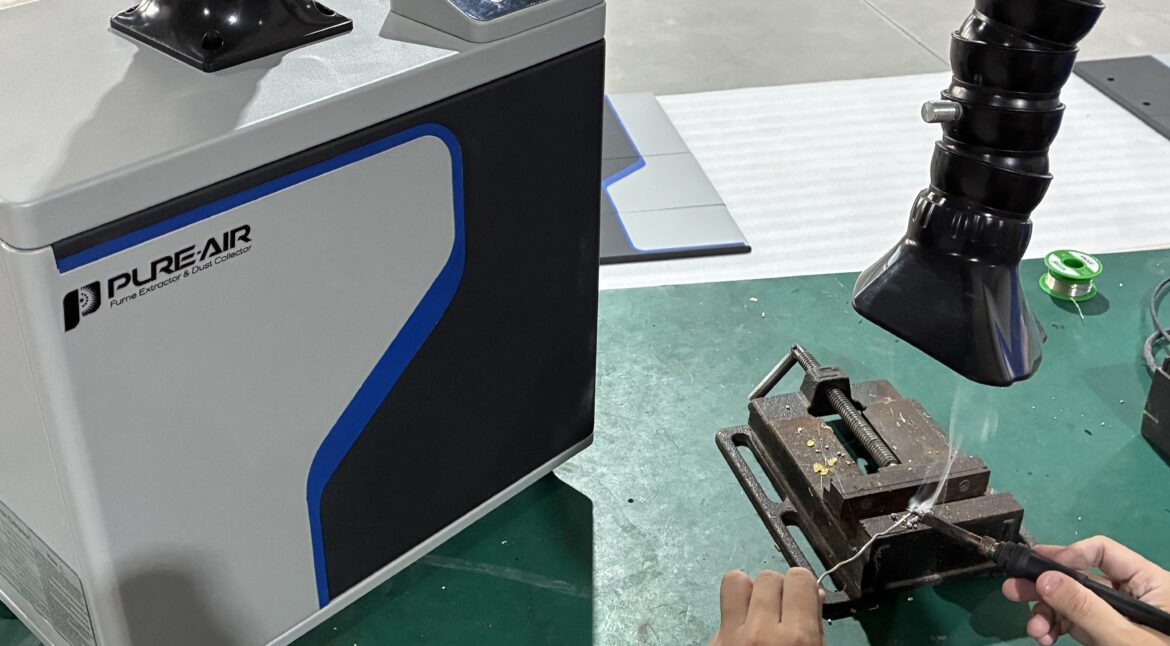
Modern factories rely on stable production, predictable maintenance schedules, and clean working conditions. Therefore, air quality control has become a mission-critical requirement. However, many workshops still underestimate the diversity of airborne contaminants. Welding shops focus on fumes, CNC machining plants worry about fine powder, and battery factories fight ultra-fine particles. Yet all these contaminants often appear in the same building. Consequently, a true industrial dust extraction machine must handle a wide spectrum of particle types, chemical compositions, and dynamic airflow demands.
This article explores the engineering foundation behind such systems. It explains why multi-stage filtration matters, how airflow dynamics determine performance, and why industrial buyers should evaluate contaminants before choosing a system. Furthermore, it helps B2B procurement teams understand why premium machines reduce downtime, extend filter life, improve safety, and support long-term cost control.
1. Why Modern Factories Need High-Capability Dust Extraction
Industrial processes generate airborne hazards every second. Welding produces metal fumes. Laser cutting emits ultra-fine particles. CNC milling releases heavy chips and light powder. Electronics factories generate chemical vapors. Additive manufacturing spreads nano-scale dust. Therefore, factories must select air filtration solutions that match these varied challenges.
Although general ventilation helps, it cannot capture contaminants at the source. Thus, localized extraction has become essential. Yet not all extraction systems perform equally. Many low-cost devices capture only visible dust. Many fail when particle sizes change. Some machines lose airflow quickly under load. Others overload filters within weeks. Therefore, procurement managers must understand the contaminants first, then select a machine tested across the full particle spectrum.
2. The Range of Contaminants a True System Must Handle
A real industrial dust extraction machine must handle more than one type of dust. In fact, industrial airborne contaminants vary across three main categories: particulates, fumes, and vapors.
2.1 Welding Fumes
Welding fumes consist of vaporized metal oxides. They cool immediately and form nano-scale particles. These particles float for hours. They also penetrate deep into the lungs because of their small size. Therefore, the extraction machine must use high airflow, strong negative pressure, and HEPA filtration.
2.2 Laser Cutting Smoke
Laser cutting produces volatile organic compounds, polymer fumes, and carbon-rich particles. These particles absorb odors, cling to surfaces, and damage optics. Consequently, the system must combine mechanical filtration with activated carbon adsorption.
2.3 Grinding and Polishing Dust
Grinding produces irregular heavy particles. These particles fall quickly, but some remain airborne because of the tool speed. Therefore, the system must maintain consistent airflow even with heavy loading.
2.4 CNC Fine Powder
CNC machining, especially when cutting aluminum, generates lightweight powder. This powder floats and clogs filters quickly. Thus, the machine must use efficient pre-filters and optimized air channels.
2.5 Soldering Fumes
Soldering generates sticky resin fumes and chemical vapors. These vapors require activated carbon. Therefore, a multi-stage design is essential.
2.6 Additive Manufacturing Dust
Additive manufacturing produces extremely fine dust. Particle sizes can reach the nanoscale. HEPA filters must meet H13 or higher standards.
A true industrial dust extractor must address all these contaminants without losing performance.
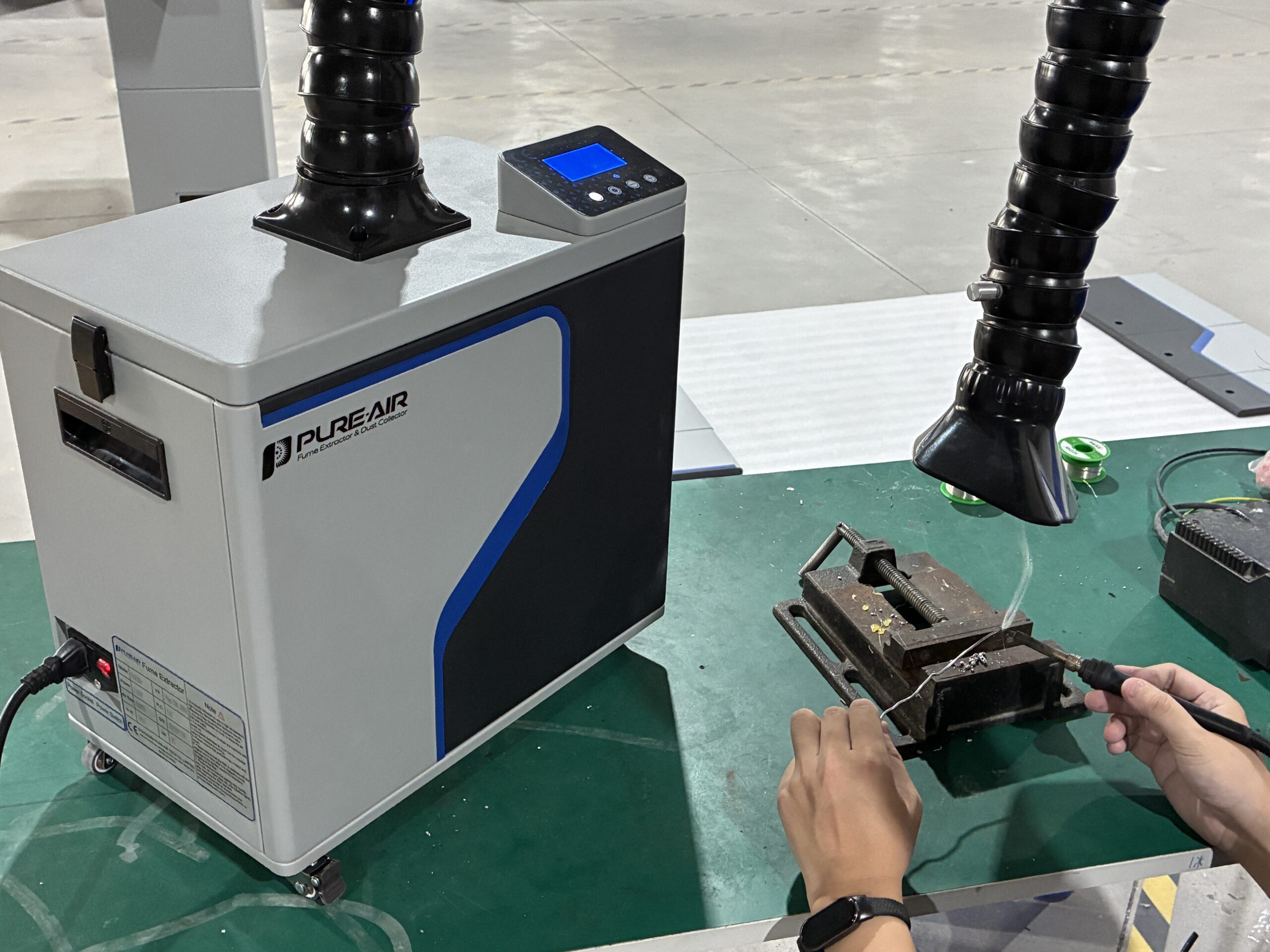

3. Engineering Requirements for True Industrial-Grade Extraction
A high-quality industrial dust extraction machine must combine airflow, filtration, structural stability, and dynamic efficiency. We analyze these requirements below.
3.1 Stable High Airflow
Airflow determines how much dust the system captures. However, the airflow must stay stable. Many low-end units show high airflow when empty. Yet when filters load, airflow collapses. Therefore, an industrial system must use a strong brushless motor, optimized impeller geometry, and a sealed system architecture.
3.2 Consistent Negative Pressure
Negative pressure allows the machine to pull contaminants into the inlet. Heavy particulates require higher negative pressure. Fumes require stable pressure. Consequently, the system must maintain pressure even as filters accumulate dust.
3.3 Multi-Stage Filtration
Multi-stage filtration ensures each particle type is captured in the correct layer. We describe the standard configuration:
-
Pre-filter blocks large dust.
-
The medium filter stops fine powder.
-
HEPA filter captures ultra-fine particles.
-
Activated carbon adsorbs chemical vapors.
These stages work together because each stage protects the next stage. Therefore, filter life increases significantly.
3.4 Anti-Clogging Air Channels
Heavy industrial dust blocks filters quickly. Good systems include optimized internal airflow paths. Smooth channels reduce pressure drop. Pre-filter baskets trap large debris. Consequently, the HEPA filter stays clean longer.
3.5 Reinforced Structure
Industrial workshops contain vibration sources, high temperatures, and chemical exposure. Therefore, the housing must use anti-corrosion metal, sealed electronic boxes, and wear-resistant casters. These details ensure stable operation under extreme conditions.
4. Multi-Stage Filtration: Why It Works Better Than Single-Stage Designs
Many low-cost systems use single-stage filtration. Such designs fail when contaminants vary. To understand why multi-stage systems excel, we analyze the physics behind each layer.
4.1 Pre-Filters Reduce System Load
Pre-filters capture large dust at low cost. If they did not exist, the HEPA filter would clog immediately. Therefore, the pre-filter protects long-term airflow stability.
4.2 HEPA Captures the Most Dangerous Particles
HEPA filters trap particles through interception, impact, and diffusion. These mechanisms capture nano-scale metal fumes and laser smoke. Therefore, HEPA ensures consistent purification efficiency.
4.3 Activated Carbon Removes Harmful Vapors
Activated carbon adsorbs VOCs and toxic gases. Many industrial processes produce these vapors. Therefore, carbon is essential for safe air quality.
4.4 Multi-Stage Synergy Improves Efficiency
The stages support each other. As a result, the system maintains stable filtration efficiency across months rather than days.
5. Airflow Dynamics: Why Extraction Distance Matters
Dust extraction depends on distance. The closer the inlet is to the dust source, the better the capture efficiency. Welding fumes rise fast. CNC powder spreads widely. Grinding dust travels horizontally. Therefore, the extraction machine must position its nozzle correctly. Additionally, flexible extraction arms play a key role. They maintain direction, angle, and stability. Consequently, source capture becomes more reliable.
6. Real-World Industrial Environments Require Adaptive Systems
Factories rarely generate only one type of dust. Therefore, extraction machines must adapt to many conditions.
6.1 Automotive Welding Workshops
These workshops generate metal fumes, spatter dust, and oil mist. They need strong negative pressure and flame-retardant filters.
6.2 CNC Machining Centers
CNC machines produce aluminum powder, steel dust, and coolant mist. They require quick-change filters and pre-separation structures.
6.3 Battery and Electronics Factories
These facilities produce toxic vapors and fine powder. They need HEPA H13 and high-capacity carbon filters.
6.4 Laser Cutting Workshops
Laser processes create particle and gas hybrids. They need strong extraction airflow and chemical filtration.
6.5 Polishing and Surface Finishing Systems
These processes generate heavy particulates. They require pre-filters and reinforced motors.
A true industrial dust extraction machine performs well in all these environments.
7. Key Metrics Procurement Teams Should Evaluate
When selecting a dust extractor, buyers must compare important metrics, not just price.
7.1 Airflow (m³/h)
Higher airflow improves capture efficiency.
7.2 Negative Pressure (Pa)
Higher pressure improves extraction distance.
7.3 Filter Area (m²)
Larger HEPA surface increases service life.
7.4 Noise Levels
Low-noise designs improve operator comfort.
7.5 Filter Replacement Cost
High-quality units reduce long-term expenses.
7.6 Machine Durability
Reinforced housings survive heavy use.
7.7 Mobility
Factories require machines that move easily.
These metrics ensure buyers choose machines that match their exact process.
 8. The Cost of Not Using a True Industrial Dust Extraction Machine
8. The Cost of Not Using a True Industrial Dust Extraction Machine
Factories that ignore air purification face significant risks.
8.1 Poor Air Quality Causes Health Damage
Nano-particles damage the lungs. VOCs irritate eyes and skin. Long-term exposure causes chronic issues. Therefore, improving air quality protects workers.
8.2 Tools Wear Faster
Fine dust enters machines and damages bearings. Spindles lose precision. Laser lenses degrade. Therefore, clean air extends equipment life.
8.3 Production Becomes Unstable
Dust affects sensors and computer systems. Therefore, stable dust control improves reliability.
8.4 Downtime Increases
Filters clog. Machines overheat. Operators lose time cleaning. Therefore, a proper extraction system reduces downtime.
9. Why PURE-AIR Systems Deliver Industrial-Grade Performance
PURE-AIR designs industrial dust extraction machines for welding, laser cutting, CNC machining, and precision manufacturing. Our systems use:
-
High-pressure brushless motors
-
Multi-stage filtration
-
Large HEPA filter area
-
High-grade activated carbon
-
Anti-clogging air channels
-
Reinforced metal construction
-
Intelligent control systems
Therefore, PURE-AIR systems support long-term industrial production with stable filtration efficiency.
Conclusion: A True Industrial Dust Extraction Machine Must Handle Everything
Industrial environments generate many different contaminants. Welding fumes behave differently from CNC powder. Laser smoke differs from grinding dust. Therefore, a real industrial dust extraction machine must capture all particle types with stable performance. Multi-stage filtration, optimized airflow, strong negative pressure, and reinforced structures form the foundation of such systems.
For B2B buyers, selecting a proven extraction solution reduces equipment wear, protects workers, cuts maintenance costs, and improves production quality. Consequently, investing in a high-performance extractor delivers long-term value across the entire factory.





